In today’s digital age, data is the cornerstone of any business. With the exponential growth of data, organizations need a robust and reliable storage solution to store, access, and manage their valuable information.
Meet Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) – a game-changing cloud storage service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). In this blog post, we will explore the power of Amazon EFS and how it can revolutionize the way your business handles its storage needs.
Table of Contents
Designed to provide scalable and highly available file storage, Amazon EFS offers a versatile solution for businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re looking for seamless data sharing across multiple instances, improved throughput performance, or strong data consistency, EFS has got you covered.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore the key features and benefits of Amazon EFS, including its integration with other AWS services, file system performance, security and access control, and cost considerations. Moreover, we’ll walk you through the steps of setting up and managing an EFS file system.
Whether you’re a developer, sysadmin, or simply curious about cloud storage solutions, this article will equip you with all the knowledge you need to make the most out of Amazon EFS. So, let’s dive in and unlock the potential of this powerful AWS service.
What is Amazon EFS?
Amazon EFS is a file-level storage service that allows multiple EC2 instances to access and modify files concurrently. It’s designed for high throughput and low latency applications, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from web hosting to big data analytics.
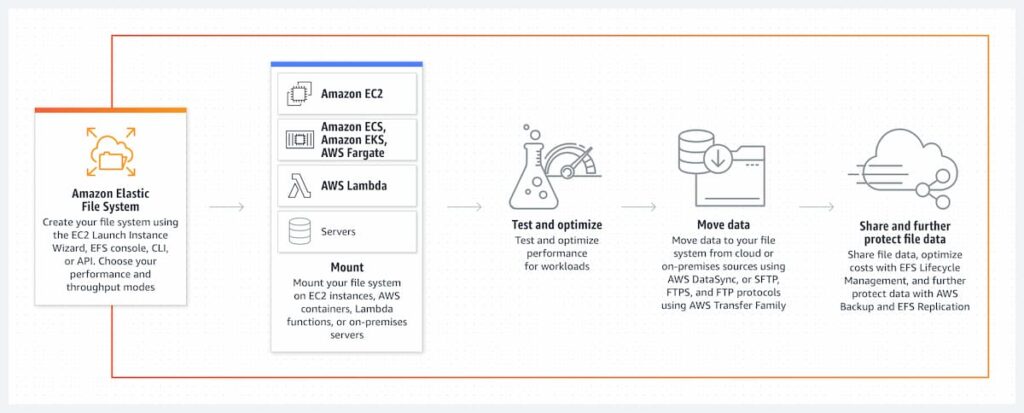
Advantages of Using Amazon EFS
Amazon EFS offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for businesses.
Scalable File Storage
Firstly, EFS provides scalable file storage, allowing you to store petabytes of data without worrying about capacity limits. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from content management systems to big data analytics.
High Availability
Secondly, EFS ensures high availability, meaning your data is accessible at all times. It automatically replicates your files across multiple availability zones, reducing the risk of data loss or downtime. This level of reliability is crucial for businesses that rely on uninterrupted access to their files.
Strong Data Consistency
Lastly, EFS offers strong data consistency, ensuring that changes made to files are immediately visible to all instances accessing the file system. This eliminates the need for complicated synchronization mechanisms and simplifies the development process.
Amazon EFS provides a robust and scalable solution for businesses that require reliable and high-performance file storage. Its advantages make it an ideal choice for a wide range of use cases.
Common Use Cases for Amazon EFS
Amazon EFS can be used in various scenarios, making it a versatile solution for different industries and applications.
Web Hosting
One common use case is web hosting. With EFS, you can easily store and serve website files across multiple instances, ensuring consistent performance and reliability. This is particularly useful for websites with high traffic or those that require dynamic content generation.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Another use case is content management systems (CMS). EFS allows multiple instances to access and modify files simultaneously, facilitating collaboration and ensuring data consistency. Whether you’re running a small blog or a large enterprise CMS, EFS can handle your storage needs.
Big Data Analytics
Additionally, EFS is well-suited for big data analytics. Its scalability and high throughput performance enable efficient processing of large datasets. With EFS, you can store and analyze vast amounts of data without worrying about capacity limitations or performance bottlenecks.
These are just a few examples of the many use cases for Amazon EFS. Its flexibility and scalability make it suitable for a wide range of applications, making it a valuable tool for businesses across industries.
Key Features of Amazon EFS
- Scalability: Unlike traditional storage systems that have fixed capacities, EFS scales on-the-fly. As you add more data, EFS expands, ensuring you never run out of storage space.
- High Availability: In the unpredictable world of digital data, EFS stands out by replicating data across several availability zones. This not only ensures data durability but also guarantees its availability even if one zone experiences issues.
- Strong Data Consistency: In distributed systems, data consistency is a challenge. EFS addresses this by ensuring that once a write operation is acknowledged, any subsequent read will reflect that write.
- Integration with AWS Services: EFS isn’t an isolated service. It’s woven into the fabric of AWS, integrating seamlessly with services like Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, and Amazon ECS. This interconnectedness allows developers to create holistic solutions that leverage the strengths of multiple AWS services.
Why Choose Amazon EFS?
The cloud storage landscape is vast, but EFS offers distinct advantages:
Scalable File Storage
Traditional storage solutions often require forecasting of storage needs, leading to over-provisioning or capacity issues. EFS eliminates this guesswork, scaling automatically with your data.
Shared File Access
Collaboration is the bedrock of modern development and business processes. EFS’s shared file access ensures that teams can work on datasets concurrently without data inconsistency issues.
Data Replication
Data is the new gold, and its loss can be catastrophic. EFS’s automatic replication across multiple zones ensures that your data is always safe and accessible.
POSIX Compatibility
For Linux-based applications, POSIX compatibility is crucial. EFS supports a broad range of POSIX file system features, ensuring that migrating existing applications to the cloud is smooth.
Performance Considerations for Amazon EFS
Amazon EFS is inherently designed for high performance, but like any system, its true potential is unlocked when you understand its intricacies and tailor it to your specific needs.
Performance Modes
EFS provides two distinct performance modes to cater to a variety of application needs:
- General Purpose (GP): This mode is the default choice and is optimized for latency-sensitive use cases. It’s ideal for a broad spectrum of workloads, including web servers, content management systems, and home directories. The GP mode provides a balanced approach, ensuring that most applications run efficiently without any additional configuration.
- Max I/O: Tailored for high-performance, data-intensive operations, the Max I/O mode scales to higher levels of aggregate throughput and operations per second. This makes it perfect for large-scale data processing tasks, such as big data analytics, media processing, and scientific simulations. While it might introduce slightly higher latencies compared to the GP mode, the trade-off is often worth it for the sheer performance boost in specific scenarios.
Throughput Capacity
Understanding and managing throughput is crucial for maintaining optimal performance:
- Bursting Throughput: EFS file systems can burst to high throughput levels for short periods, which is often sufficient for many workloads. This model allows sporadic high-throughput activities without incurring additional costs.
- Provisioned Throughput: For applications with consistent high-throughput demands, EFS allows you to provision specific throughput levels. This ensures that your file system can handle the load at all times, providing consistent performance.
Network Connectivity
The physical proximity of resources in the cloud can significantly impact performance:
- Zone Matching: Deploying your EC2 instances and EFS file systems within the same availability zone is recommended. This minimizes data transit times, reducing latency and ensuring faster data access.
- VPC Peering: If your resources span multiple VPCs, consider setting up VPC peering to ensure efficient data transfer between your EFS and other AWS resources.
Monitoring and Cost-Effective Strategies
Ensuring the health and cost-effectiveness of your EFS systems is paramount. AWS offers tools and strategies to help you achieve this:
Amazon CloudWatch
CloudWatch is a monitoring service that provides actionable insights:
- Metrics Monitoring: Track key metrics like read and write operations, bytes read or written, and more. This helps in understanding the load on your EFS and making informed decisions.
- Alarms: Set up alarms to be notified of any anomalies or when certain thresholds are breached. This proactive approach ensures that you can address potential issues before they escalate.
Cost Optimization
EFS’s pricing model is based on the storage used and the amount of data transferred. However, there are ways to optimize these costs:
- Lifecycle Management Policies: Implement policies to transition older, less-accessed data to the EFS Infrequent Access storage class. This class is more cost-effective and is ideal for data that isn’t accessed often but is still important.
- Monitor Provisioned Throughput: Regularly review the provisioned throughput levels. If your file system consistently uses less than the provisioned level, consider reducing it to cut costs.
- Delete Unneeded Data: Regularly audit and remove unnecessary data. Not only does this save on storage costs, but it also ensures that your file system remains organized and efficient.
By leveraging AWS’s monitoring tools and implementing cost-saving strategies, you can ensure that your EFS remains both performant and cost-effective.
Exploring Alternatives to Amazon EFS
While Amazon EFS is a robust and versatile storage solution, it’s essential to recognize that AWS offers a suite of storage services, each tailored for specific use cases. Depending on your application’s requirements, another AWS storage solution might be a better fit. Let’s delve deeper into some of these alternatives and understand their unique offerings.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Amazon EBS is a block storage service designed to be used with Amazon EC2 instances. Here’s what sets EBS apart:
- Performance: EBS volumes are designed to offer low-latency, high-throughput performance, making them ideal for workloads that require frequent read/write operations with small data sets.
- Durability and Availability: EBS volumes are automatically replicated within their availability zone, protecting you from component failures and ensuring high availability.
- Snapshot Capabilities: You can take point-in-time snapshots of EBS volumes, which are stored in Amazon S3. These snapshots can be used for backups, disaster recovery, or migrating data across regions.
- Use Cases: EBS is particularly suited for databases, enterprise applications, containerized applications, big data analytics engines, and more.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon S3 is an object storage service known for its scalability, data availability, and security features. Here’s why you might consider S3:
- Scalability: S3 can store an unlimited amount of data, making it perfect for applications that generate vast amounts of non-structured data.
- Data Lifecycle Policies: With S3, you can automate the transition of data between different storage classes, ensuring cost-effectiveness without compromising data availability.
- Data Transfer Acceleration: S3 offers features like Transfer Acceleration for faster uploads/downloads and integrates seamlessly with Amazon CloudFront for content distribution.
- Event-driven Computing: You can trigger AWS Lambda functions based on events in S3, like the creation or deletion of an object, allowing for automated workflows.
- Use Cases: S3 is ideal for backup and archival, content distribution, static website hosting, big data storage, and much more.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Storage Solution
- Data Access Patterns: Do you need block-level access, or would object storage suffice? EBS provides block storage, S3 offers object storage, while EFS offers file-level storage.
- Performance Requirements: If your application requires high IOPS and low-latency access, EBS might be more appropriate. For scalable file storage with shared access capabilities, EFS is the go-to solution.
- Data Durability and Availability: While all AWS storage solutions offer high durability and availability, the specifics vary. For instance, S3 boasts 99.999999999% (11 9’s) durability over a given year.
- Cost: Each service has a different pricing model. EBS charges for provisioned storage and I/O operations, S3 charges based on stored data and requests, and EFS has pricing based on the amount of data stored.
- Integration with Other AWS Services: Depending on your architecture, you might need a storage solution that integrates seamlessly with other AWS offerings. For instance, if you’re building a serverless application, the tight integration between S3 and Lambda might be beneficial.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is a powerful and versatile storage solution offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It provides scalable, highly available, and secure file storage, making it an ideal choice for businesses of all sizes.
Furthermore, we examined the key features of Amazon EFS, such as its integration with other AWS services, performance modes, encryption, and access control. We walked through the process of setting up and configuring EFS, ensuring that you have all the information you need to get started.
With this comprehensive guide, you are now equipped with all the knowledge you need to make the most out of Amazon EFS. Whether you’re a developer, sysadmin, or simply curious about cloud storage solutions, Amazon EFS offers a powerful, scalable, and secure file storage solution that can meet your needs. So, dive in and unlock the potential of Amazon EFS today!




